An undersea volcano located approximately 470 kilometers off the coast of Oregon, Axial Seamount, is showing signs of an impending eruption. Researchers have identified critical indicators such as ground deformation, increased seismic activity, and magma buildup beneath the surface. These findings suggest that the volcano could erupt as early as 2025, marking a significant milestone in volcanic monitoring, where predictions of eruptions are rarely this precise.
Axial Seamount, one of the world’s most closely observed submarine volcanoes, has been the subject of continuous study through state-of-the-art instruments installed on the seafloor. These devices record real-time data, enabling scientists to track its activity.
A study presented at the American Geophysical Union meeting titled Axial Seamount Has Suddenly Woken Up! An Update on the Latest Inflation and Seismic Data and a New Eruption Forecast reveals that the volcano is exhibiting patterns similar to those observed before its 2015 eruption. Surface swelling and swarms of earthquakes are among the signals indicating that a repeat event may be imminent.
The possibility of an eruption has also driven advancements in volcanic prediction techniques. Artificial intelligence is being employed to analyze seismic data from the 2015 eruption, identifying patterns associated with magma movement. These AI-driven insights are expected to improve forecasting accuracy. Axial Seamount serves as a testing ground for these innovations, which could eventually benefit monitoring efforts for other volcanic systems worldwide.
Although Axial Seamount is not an immediate threat to human populations, its activity holds global sig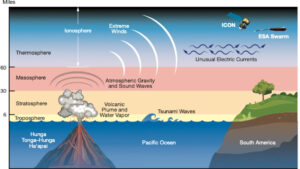 nificance. The 2022 eruption of the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai volcano, which triggered a tsunami across the Pacific, highlights the importance of being prepared for such events. Enhanced forecasting capabilities could provide crucial early warnings to mitigate risks for vulnerable coastal regions.
nificance. The 2022 eruption of the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai volcano, which triggered a tsunami across the Pacific, highlights the importance of being prepared for such events. Enhanced forecasting capabilities could provide crucial early warnings to mitigate risks for vulnerable coastal regions.
As researchers continue to monitor Axial Seamount, the knowledge gained from its activity is expected to contribute to advancements in volcanic science and disaster preparedness. The findings could have far-reaching implications, providing valuable insights into the complex dynamics of undersea volcanoes and their potential impacts.
