Earth’s Magnetic North Pole Continues Its Drift Toward Siberia: How This Ongoing Shift Could Impact Global Navigation and Technology
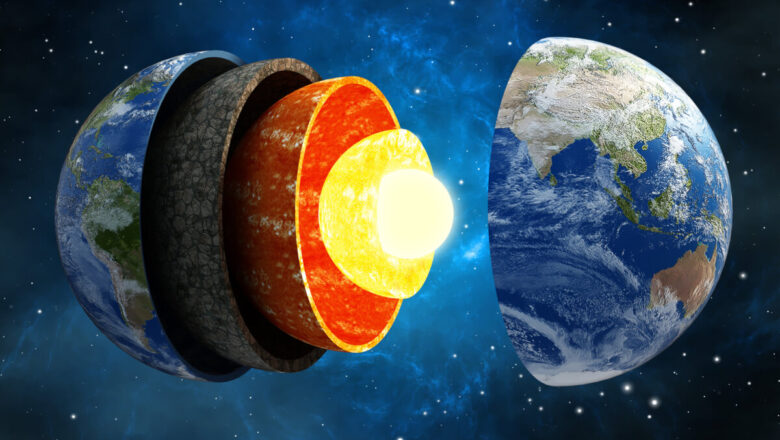
Earth’s magnetic north pole has moved again, drawing closer to Siberia, according to the latest update of the World Magnetic Model (WMM). This shift could have significant implications for global navigation systems, including those used by commercial aviation and GPS devices.
Unlike the fixed geographic North Pole, magnetic north is influenced by the turbulent movement of molten iron in Earth’s core. The pole has been drifting for centuries, but its speed increased dramatically in the 1990s, reaching a peak of 34.2 miles (55 km) per year before slowing to around 21.7 miles (35 km) per year by 2015.
The WMM, updated every five years, ensures accurate navigation for planes, ships, and military operations. If updates are delayed, navigation errors could occur. Dr. Arnaud Chulliat, a sen...