Organic Pioneer: Farmer Earns Lakhs from India First Sindoor Farm
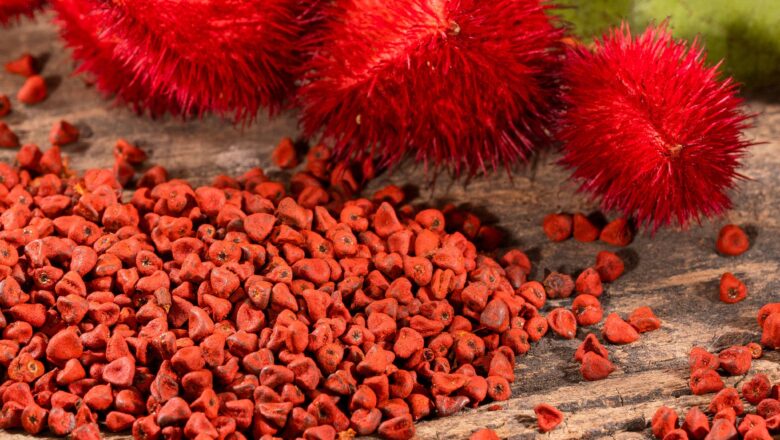
FATEHPUR, UTTAR PRADESH – In a unique blend of entrepreneurship and traditional wisdom, Ashok Tapaswi, a former city resident, has transformed his barren ancestral land in Fatehpur into India's first organic sindoor farm. By cultivating Annatto trees, a medicinal plant with vibrant red seeds, Tapaswi has created a profitable business while addressing the health risks associated with chemical-laden cosmetics.
Tapaswi’s journey began after he discovered that synthetic sindoor in the market often contains harmful chemicals like lead and mercury, which can cause skin irritation and hair loss. Inspired by Ayurveda, he decided to grow Annatto, which has long been used to produce a natural, chemical-free alternative. Starting with just a handful of saplings, his farm now flourishes with over 4...